Delve into the captivating realm of areas of regular polygons worksheet answers, where mathematical precision meets geometric elegance. This comprehensive guide unveils the fundamental concepts, formulas, and problem-solving techniques that illuminate the intricacies of this captivating topic, empowering you to conquer any challenge with confidence.
As we embark on this intellectual journey, we will explore the profound relationship between the number of sides and the area of a regular polygon, equipping you with the knowledge to tackle real-world applications with finesse.
Areas of Regular Polygons: Areas Of Regular Polygons Worksheet Answers
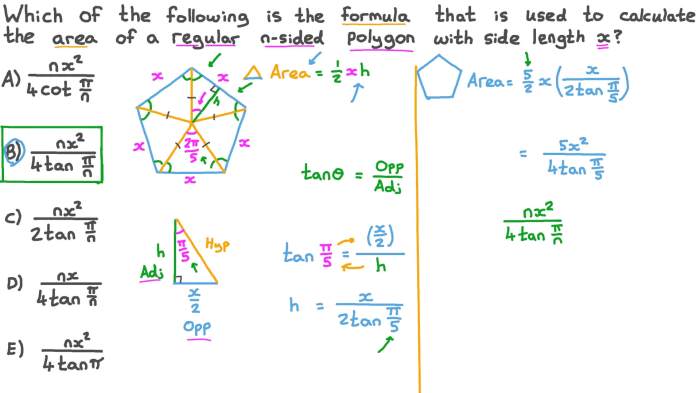
Area is a measure of the two-dimensional space occupied by a figure. In the case of regular polygons, the area is the amount of space enclosed within the polygon’s sides.
Calculating the Area of Regular Polygons
The area of a regular polygon can be calculated using the following formulas:
- Triangle:
A = (1/2) – b – h
where b is the length of the base and h is the height
- Square:
A = s 2
where s is the length of one side
- Rectangle:
A = l – w
where l is the length and w is the width
- Pentagon:
A = (1/4) – s 2– sqrt(5(5 + 2 – sqrt(5)))
where s is the length of one side
- Hexagon:
A = (3 – sqrt(3)) / 2 – s 2
where s is the length of one side
The number of sides in a regular polygon affects its area. As the number of sides increases, the area of the polygon also increases.
Worksheet Problems and Solutions
Problem 1:Find the area of a square with a side length of 5 cm.
Solution:A = s 2= 5 2= 25 cm 2
Problem 2:Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 6 cm and a width of 4 cm.
Solution:A = l – w = 6 – 4 = 24 cm 2
Problem 3:Find the area of a regular hexagon with a side length of 3 cm.
Solution:A = (3 – sqrt(3)) / 2 – s 2= (3 – sqrt(3)) / 2 – 3 2= 9 – sqrt(3) cm 2
Example Problems and Applications, Areas of regular polygons worksheet answers
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find the area of a floor that is tiled with square tiles, each with a side length of 30 cm. The floor is 5 meters long and 4 meters wide. | Convert the length and width to centimeters: 5 meters = 500 cm, 4 meters = 400 cm. Calculate the number of tiles in each row: 500 cm / 30 cm = 16.67 tiles. Calculate the number of tiles in each column: 400 cm / 30 cm = 13.33 tiles. Calculate the total number of tiles: 16.67 tiles
13.33 tiles = 222.22 tiles. Calculate the area of one tile 30 cm 30 cm = 900 cm2. Calculate the total area of the floor 900 cm 2
|
| Find the area of a triangular garden with a base of 10 feet and a height of 8 feet. | Convert the base and height to inches: 10 feet = 120 inches, 8 feet = 96 inches. Calculate the area: A = (1/2)
|
Extensions and Variations
Variation 1:Find the area of an irregular polygon by dividing it into triangles and rectangles and calculating the area of each shape separately.
Variation 2:Estimate the area of a regular polygon by using a formula that approximates the area of a circle. For example, the area of a regular hexagon can be approximated as A ≈ (6/π) – r 2, where r is the radius of the circle that circumscribes the hexagon.
Activity:Design a project where students create a mosaic or tessellation using regular polygons of different sizes and shapes. Encourage them to explore the relationship between the number of sides and the area of the polygons they use.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the formula for calculating the area of a regular polygon?
A = (1/2) – P – a, where A is the area, P is the perimeter, and a is the apothem (the distance from the center to a side).
How can I determine the area of an irregular polygon?
Divide the irregular polygon into regular polygons or triangles, calculate the area of each part, and then sum them up to find the total area.
What are the real-world applications of understanding areas of regular polygons?
Architecture, tiling, land surveying, graphic design, and engineering all rely on the principles of regular polygon areas.